| Citation: | Manman CAO, Naifa LIU, Xiaoli WANG, Mengmeng GUAN. 2010: Genetic diversity and genetic structure of the Daurian Partridge (Perdix dauuricae) in China, assessed by microsatellite variation. Avian Research, 1(1): 51-64. DOI: 10.5122/cbirds.2009.0005 |
The Daurian Partridge (Perdix dauuricae) is a kind of hunting bird with high economic value. Genetic diversity and structure in the Daurian Partridge were studied by analyzing eight microsatellite loci in 23 populations found throughout the range of the species in China. The objectives were to evaluate the consequences on genetic diversity and differentiation of Daurian Partridge populations and to obtain a profound genetic insight for future management decisions and for effective measures to protect and exploit Daurian Partridges. The results showed that microsatellites were polymorphic in all Daurian Partridge populations, with a high level of genetic diversity over all the loci, especially in the Qaidam Basin populations which have the highest level of diversity. Significant genetic divergence was observed among different groups as well as between populations within the same group; most pairwise FST values were highly significant. Both phylogenetic trees and Bayesian clustering analyses revealed clear differentiation among the 23 populations of the Daurian Partridge, which were classified into two genetically differentiated groups. A bottleneck analysis indicated that Daurian Partridge populations have experienced a recent bottleneck. Our study argues that the Qaidam populations, North China populations, JN population, ZJC population, and Liupan Mountain populations should be paid special attention in order to retain adequate population sizes for maintaining genetic diversity.
Conservation genetics is a discipline that uses genetic theories and methods to investigate and protect biological diversity (Woodruff, 1989). Largely, the aim is to protect genetic diversity and evolutionary processes (Avise, 1994). Knowledge of genetic diversity and population genetic structures in species is important for understanding spatial patterns and the formulation of conservation strategies. Genetic diversity and structures are affected by various factors, including ecological traits such as breeding systems, life forms, distribution patterns of populations and individuals, historical shifts in distribution caused by climate changes, especially those associated with ice ages and anthropogenic effects, such as habitat fragmentation and isolation (Hamrick and Godt, 1989; Hamrick et al., 1992; Heuertz et al., 2004). In particular, large-scale environmental changes are thought to have a major impact on species distributions and population divergence since the beginning of the Quaternary period (Avise and Walker, 1998; Hewitt, 2004) and these have affected their genetic diversity and structure to a considerable extent (Comes and Kadereit, 1998; Hewitt, 2000).
Molecular markers provide important measures of genetic characteristics of populations. Population genetic theory predicts that when the size of a population declines, its genetic diversity is also likely to be reduced by genetic drift, but the number of alleles is more strongly affected by this decline than heterozygosity (Nei et al., 1975; Maruyama and Fuerst, 1985). Microsatellite markers generally have far higher polymorphism than other molecular markers (Turner et al., 2003), facilitating higher resolution analysis. This fact could be more suitable for detecting phenomena such as reductions in genetic diversity associated with reductions in population size through founding events or population bottlenecks during expansions or reductions of the range of a species. As well, the availability of microsatellite markers can be used to identify multilocus genotypes with higher resolution than other molecular markers. Besides, their abundance, codominance and an unambiguous scoring of alleles (Tautz, 1989), inherited through both parents, can better reflect genetic structuring in both sexes. These features provide the basis for their successful application in a wide range of applied fields of biology and medicine (Chistiakov et al., 2006).
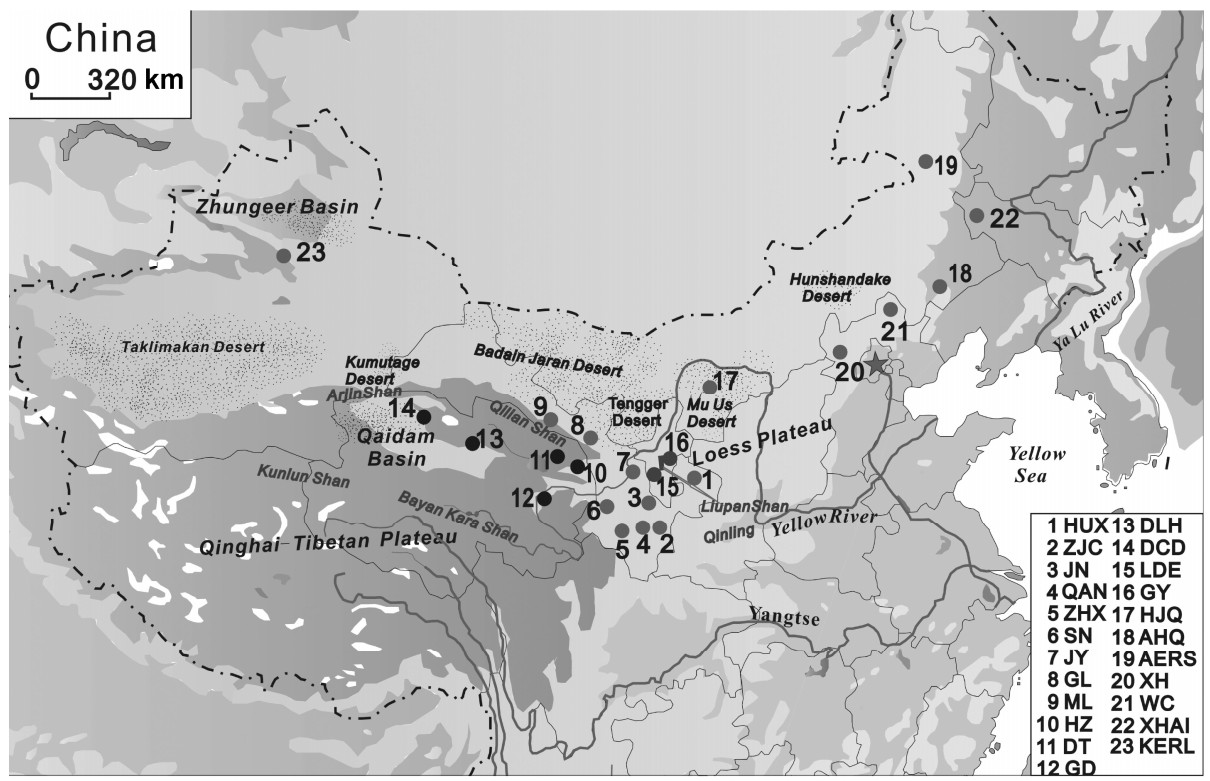
The Daurian Partridge (Perdix dauuricae) (Galliformes: Phasianidae) inhabits grassy and wooded steppes, up to at least 3000 m elevation, but avoids steep mountain slopes as well as deserts (Madge and McGowan, 2002). Belts of foothills and their adjacent plains with meadows, plantations and river valleys are favored, but the partridge is also found on grassy slopes of foothills and mountain meadows (Johnsgard, 1988). The Daurian Partridge is distributed in the Asian grasslands from the Russian Altai east to Transbaicalia, Amurland and Ussuriland, and south to Manchuria, Mongolia (Johnsgard, 1988). This species is found throughout northern China, i.e., in northwestern and western Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia, the northeastern China plains, the North China plains, Gansu and Qinghai provinces (Zheng, 1978) (Fig. 1). This species was introduced locally to the Manilla area in the Philippines (Johnsgard, 1988).

The Daurian Partridge is a kind of hunting bird with high economic value. Research has shown that the size of populations tends to decline (Zhang and Wu, 1992; Zhao et al., 1992). The species has been included in the terrestrial wildlife list for it has beneficial and important economic and scientific values. There are no reports about this species abroad and only a few reports about its life history have been published in China (Zhang et al., 1994; Sun et al., 1996, 1998; Zhang and Liang, 1997). Published reports about information on genetic diversity and the structure of Daurian Partridge are even more scarce.
In our study, we examined the genetic diversity and structure in Daurian Partridge by analyzing eight microsatellite markers in 23 populations, distributed throughout most of the range of the species. Our objective, to assess the genetic diversity and structure of Daurian Partridge, enables us to obtain a provisional theoretical basis and some genetic background information for future management decisions and for suitable and effective measures to protect and exploit the Daurian Partridge.
A total of 285 tissue or feather samples were collected from the various distribution areas of the species (Table 1). Sample locations of the populations are shown in Fig. 1. We stored samples individually at –20℃ in test tubes containing 95% ethanol. Total DNA was extracted using a guanidinium thiocianate and diatomaceus earth protocol (Gerloff et al., 1995).
| Population number |
Location | Abbreviation | Group name | Latitude | Longitude | Sample size |
| Gansu Loess Plateau | ||||||
| 1 | Huanxian County | HUX | A | 36°55.37′ | 101°41.08′ | 10 |
| 2 | Zhangjiachuan | ZJC | A | 34°59.41′ | 106°12.43′ | 15 |
| 3 | Jingning | JN | A | 35°31.19′ | 105°43.57′ | 13 |
| 4 | Qin'an | QAN | A | 34°51.31′ | 105°40.10′ | 17 |
| 5 | Zhangxian County | ZHX | A | 34°50.78′ | 104°27.89′ | 15 |
| 6 | Su'nan | SN | A | 38°50.13′ | 99°36.56′ | 15 |
| 7 | Jingyuan | JY | A | 37°57.46′ | 101°35.07′ | 15 |
| 8 | Gulang | GL | A | 37°28.13′ | 102°53.51′ | 16 |
| 9 | Minle | ML | A | 38°25.50′ | 100°48.46′ | 15 |
| Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau | ||||||
| 10 | Huzhu | HZ | A | 37°7.07′ | 100°17.51′ | 11 |
| 11 | Datong | DT | A | 36°51.07′ | 102°9.07′ | 9 |
| 12 | Guide | GD | A | 35°56.03′ | 101°28.37′ | 10 |
| 13 | Delingha | DLH | A | 32°22.13′ | 97°21.24′ | 7 |
| 14 | Dachaidan | DCD | A | 37°50.01′ | 95°17.53′ | 10 |
| Liupan Mountain | ||||||
| 15 | Longde | LDE | B | 35°33.21′ | 106°2.46′ | 15 |
| 16 | Guyuan | GY | B | 36°1.00′ | 106°14.34′ | 15 |
| Inner Mongolia | ||||||
| 17 | Hangjinqi | HJQ | B | 39°50.55′ | 108°43.49′ | 16 |
| 18 | Aohanqi | AHQ | B | 42°17.05′ | 119°54.00′ | 15 |
| 19 | Aershan | AERS | B | 47°10.39′ | 119°56.37′ | 10 |
| North China Plain | ||||||
| 20 | Xuanhua | XH | B | 40°29.33′ | 115°6.19′ | 7 |
| 21 | Weichang | WC | B | 42°5.38′ | 117°31.39′ | 8 |
| Northeast China Plain | ||||||
| 22 | Xianghai | XHAI | B | 45°1.84′ | 122°24.34′ | 16 |
| Xinjiang | ||||||
| 23 | Kuerler | KERL | B | 41°45.35′ | 86°8.05′ | 5 |
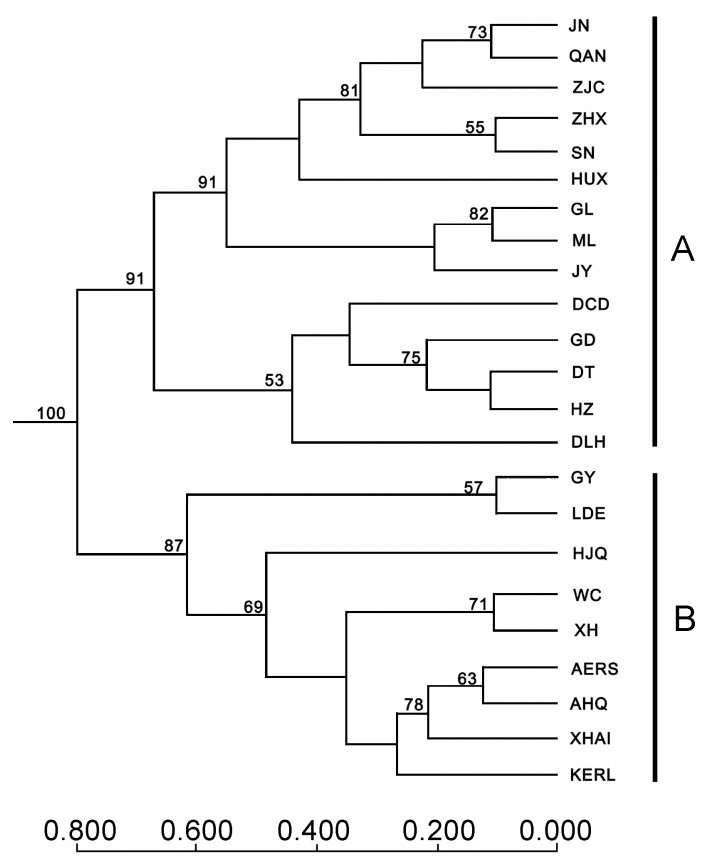
| The group names A and B correspond to the cluster names in Fig. 2. | ||||||
We screened 14 microsatellite loci, developed in the domestic chicken and quail, for use in the partridge. Eight of these loci amplified successfully and were polymorphic in our sample set. All samples were genotyped by PCR amplifications of eight variable microsatellite primers genome: (MCW104, MCW280, MCW323, AF12114, UBC0002, UBC0006, GUJ0049, GUJ0059). Primer sequences and information on markers can be retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm. nih.gov/sites/entrez. PCR was performed in 50-μL reaction mixtures containing 1.5–2.3 mM MgCl2, 0.6 μM primer pair, 0.4 mM dNTP, 100 ng of the DNA template, 0.4 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Sigma) and 1× PCR buffer (Sigma). The PCR protocol used was: 1) initial DNA denaturation at 94℃ for 4 min; 2) 35 successive cycles of strand denaturation at 94℃ for 40 s; 3) primer annealing at 45–60℃ for 40 s and 4) DNA extension at 72℃ for 45 s. A prolonged extension step at 72℃ for 6 min was added after the final cycle. Amplified products, which ran on an 8% polyacrylamide gel by electrophoresis, could be visualized by silver staining. PUC19 DNA/MspⅠ (HpaⅡ), as a size standard, ran on each gel in order to determine fragment sizes, by using Bandscan 4.30 software (http://moleco.sjtu.edu.cn).
GENETIX 4.02 (Belkhir et al., 2004; http://www.univmontp2.fr/genetix/genetix.htm) was used to examine genetic diversity over all populations of polymorphic loci, the total number of alleles detected (TA), gene diversity in the total population (HT) and average gene diversity within populations (HS) (Nei, 1987). Observed heterozygosity (HO) and expected heterozygosity (HE) were calculated across all populations at each locus and over all loci. We used the FSTAT version 2.9.3 (Goudet, 2001) to calculate the fixation index, FIS (Weir and Cockerham, 1984) across all populations at each locus and over all loci, to measure departures from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE). We tested linkage disequilibrium for all pairwise combinations of loci and genotypic differentiation using exact tests implemented in GENEPOP (Raymond and Rousset, 1995a; http://www.cefe.cnrs-mop.fr). The deviations of FIS from zero and linkage disequilibrium for all locus pairs were tested in each population by permutation tests with a sequential Bonferroni correction using FSTAT version 2.9.3 (Goudet, 2001). The tests for linkage disequilibrium were performed to validate the use of Bayesian clustering methods (Pritchard et al., 2000), which assume linkage equilibrium among loci. Similarly, to assess genetic diversity within each population, the number of alleles (A), allelic richness (AR) (El Mousadik and Petit, 1996), observed heterozygosity (HO), and unbiased expected heterozygosity (HE) (Nei, 1987) were calculated at each locus and over all loci in each population, using FSTAT. The polymorphism information content (PIC) was obtained using individual frequencies in which the alleles occur at each locus (Nei, 1978).
The significance of differences in allele frequency distributions between populations was obtained using ARLEQUIN 3.1 (Excoffier et al., 2005) exact test of population differentiation (Raymond and Rousset, 1995b) of pairwise weighted means (FST) (Weir and Cockerham, 1984) and RST (Slatkin, 1995). The gene flow (Nm) between populations was also determined using ARLEQUIN 3.1. We used hierarchical analysis of AMOVA (Michalakis and Excoffier, 1996; Excoffier et al., 2005) in ARLEQUIN 3.1 to examine variance within and between populations. This approach allowed the analysis of a population using a combination of allele frequency and molecular data or analyses solely based on allele frequencies. AMOVA calculated genetic distances based on pairwise FST indices between all pairs of sample sites. The significance of the test statistics was examined by 1000 permutations using a nonparametric approach (Excoffier et al., 2005). Variance components were extracted for the 1) among groups, 2) between sampling sites within groups and 3) within sampling sites hierarchical levels.
To estimate patterns of divergence among populations, Nei's standard genetic distance was used (Nei, 1972; Takezaki and Nei, 1996) because it makes allowances for mutations, which are likely to be a factor during the timescales considered. Evolutionary trees were constructed using UPGMA (Takezaki and Nei, 1996) through resampling among loci using a 1000 bootstrap computation. ARLEQUIN 3.1 was used to calculate inter-population divergence times allowing for unequal population sizes (Gaggiotti and Excoffier, 2000).
We used structure to infer the existence of genetically distinct clusters and assign the individuals to the clusters, using or not using the available previous population information (option USEPOPINFO = 1, or = 0), with 100000 iterations, following a burn-in period of 10000 iterations. Populations or individuals were assigned to one cluster if their proportion of membership (q) to that cluster was equal to or larger than an arbitrary threshold of 0.800.
We assessed correlations of genetic distance and geographic distances using MANTEL correlations (Mantel, 1967). We derived genetic differences as FST / (1 − FST) according to Rousset (1997) between all pairs of local populations using a MANTEL test in the program FSTAT version 2.9.3 (Goudet, 2001). This test was conducted on the data from all pairwise comparisons among populations irrespective of whether populations were allopatric or from continuous parts of the species distribution. The measures of neutral genetic divergence were pairwise multilocus RST-values (which were more informative of population differentiation than multilocus FST- values).
We used the empirical approach described by Luikart and Cornuet (1997) to detect recent population bottlenecks. In the present study, we used the Wilcoxon signed-rank test of heterozygosity of excess under the Stepwise Mutation Model (SMM), the Infinite Allele Model (IAM) and the Two Phase Model (TPM). Under the TPM, 70% of the mutations were assumed to occur under the SMM and 30% under the IAM. For each mutational model, 10000 replications were performed.
Microsatellites were polymorphic in all populations of the Daurian Partridge. The 285 individuals, representing 23 different geographic populations, produced a total of 94 alleles at the eight loci tested with an average of 11.75 alleles per locus. The eight microsatellite loci were found to be highly polymorphic, the total number of alleles detected over all populations at each locus ranging from 5 (MCW280) to 20 (UBC0006) (Table 2). On average over all loci, gene diversity in the total population (HT) was 0.75 and the average gene diversity within populations (HS) 0.72. The PIC values ranged from 0.56 (MCW280) to 0.87 (UBC0006). FIS values across all populations deviated significantly and positively from zero at seven loci and over all loci.
| Locus | TA | PIC | HT | HS | HO | FIS |
| MCW104 | 14 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.333*** |
| MCW280 | 5 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 0.309** |
| AF12114 | 11 | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.42 | 0.401 |
| UBC0006 | 20 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.185** |
| UBC0002 | 7 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.51 | 0.348** |
| GUJ0059 | 13 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.60 | 0.346*** |
| GUJ0049 | 9 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.325* |
| MCW323 | 15 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.338*** |
| Average | 11.75 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.58 | 0.323*** |
|
TA, total number of alleles; PIC, polymorphic information content; HT, gene diversity in the total population; HS, average gene diversity within populations; HO, observed heterozygosity; FIS, fixation index. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. |
||||||
High levels of genetic diversity within populations were also observed in each population (on average, A = 6.3, AR = 23, HO = 0.58, HE = 0.72; see Table 3). The mean number of alleles per locus ranged from A = 4.3 in the KERL population to A = 8.9 in the DCD population. Allelic richness ranged from a minimum AR = 3.50 in the KERL population to a maximum AR = 8.05 in the DCD population (p = 0.001; Wilcoxon signed-rank test). Expected heterozygosity ranged from 0.61 (AHQ population) to 0.81 (DLH population). The average of FIS = 0.333 was significantly positive (p < 0.05, Table 3), indicating that there were less heterozygotes than expected in the total sample (Table 3). FIS values were positive in each population and the multilocus test (Raymond and Rousset, 1995a, 1995b) showed that the HUX, ZJC, QAN, GL, GD, LDE and AHQ populations were deficient in heterozygotes (p < 0.001) (Table 3).
| Population | A | AR | Na | p | HO (SD) | HE (SD) | FIS (95% CI) |
| HUX | 7.3 | 6.50 | 3 | 8.00 | 0.55 (0.32) | 0.71 (0.21) | 0.074 (0.122–0.206) * |
| ZJC | 8.0 | 7.00 | 1 | 8.00 | 0.63 (0.29) | 0.68 (0.15) | 0.084 (0.119–0.215) * |
| JN | 8.0 | 7.00 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.66 (0.27) | 0.70 (0.09) | 0.086 (0.105–0.218) |
| QAN | 7.6 | 7.00 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.62 (0.27) | 0.71 (0.16) | 0.102 (0.107–0.325) * |
| ZHX | 7.5 | 7.00 | 0 | 7.00 | 0.58 (0.29) | 0.70 (0.14) | 0.087 (0.109–0.277) |
| SN | 7.8 | 7.00 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.60 (0.22) | 0.70 (0.22) | 0.071 (0.087–0.160) |
| JY | 7.9 | 7.15 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.56 (0.39) | 0.69 (0.19) | 0.075 (0.075–0.198) |
| GL | 7.0 | 5.95 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.58 (0.33) | 0.67 (0.22) | 0.069 (0.104–0.198) * |
| ML | 7.4 | 7.00 | 4 | 7.00 | 0.59 (0.11) | 0.62 (0.07) | 0.086 (0.195–0.396) |
| HZ | 7.0 | 6.25 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.53 (0.29) | 0.71 (0.13) | 0.092 (0.136–0.249) |
| DT | 7.0 | 6.75 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.60 (0.35) | 0.72 (0.10) | 0.073 (0.046–0.165) |
| GD | 7.1 | 6.50 | 3 | 8.00 | 0.58 (0.24) | 0.76 (0.12) | 0.084 (0.137–0.275) * |
| DLH | 8.0 | 7.55 | 5 | 8.00 | 0.67 (0.31) | 0.81 (0.11) | 0.086 (0.052–0.122) |
| DCD | 8.9 | 8.05 | 3 | 8.00 | 0.70 (0.35) | 0.78 (0.07) | 0.075 (0.021–0.200) |
| LDE | 6.1 | 5.00 | 6 | 8.00 | 0.52 (0.29) | 0.72 (0.11) | 0.087 (–0.043–0.500)* |
| GY | 6.4 | 5.75 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.56 (0.24) | 0.70 (0.13) | 0.069 (0.109–0.202) |
| HJQ | 7.0 | 6.25 | 3 | 7.00 | 0.57 (0.31) | 0.71 (0.21) | 0.097 (0.025–0.107) |
| AHQ | 7.8 | 6.75 | 1 | 8.00 | 0.53 (0.32) | 0.61 (0.25) | 0.088 (0.163–0.229) * |
| AERS | 7.3 | 6.05 | 4 | 8.00 | 0.61 (0.24) | 0.72 (0.15) | 0.067 (0.087–0.139) |
| XH | 7.0 | 6.35 | 3 | 8.00 | 0.64 (0.28) | 0.76 (0.10) | 0.071 (0.128–0.226) |
| WC | 8.7 | 8.00 | 2 | 7.00 | 0.68 (0.30) | 0.76 (0.07) | 0.112 (0.151–0.218) |
| XHAI | 7.2 | 6.25 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.46 (0.42) | 0.70 (0.17) | 0.092 (0.112–0.257) |
| KERL | 4.3 | 3.50 | 4 | 7.00 | 0.42 (0.29) | 0.70 (0.09) | 0.084 (0.025–0.231) |
| Total | – | – | – | 8 | 0.58 (0.34) | 0.72 (0.17) | 0.333 (0.201–0.379) |
| Abbreviations as in Table 1. * significant (p < 0.001) departures from HWE tested by multilocus probability test using GENEPOP. |
|||||||
Probability tests for departure from HWE, performed in each population, showed that one locus in HUX, SN (MCW323), one in JN, ML, AERS (MCW104), one in JN (UBC0006), two loci (MCW323, UBC0002) in GL, two loci (MCW280, AF12114) in KERL, three loci (MCW280, AF12114, GUJ0059) in GD were not in equilibrium (p < 0.001). After sequential Bonferroni corrections, however, non-significant (p > 0.05) departures from HWE for UBC0002 in GL, MCW280 in KERL and GD were found. Given the operation of a Wahlund effect in the pooled sample, we might have expected all loci to be affected, but perhaps to varying degrees, depending on the number of alleles and frequency distributions. It should be noted, however, that highly polymorphic loci might also be more likely to exhibit null alleles, so the possibility that null alleles are contributing to heterozygous deficits at some loci cannot be ruled out. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) among all 644 pairs of loci was tested for genotypic disequilibrium using ARLEQUIN 3.1. All loci were in LE except for three combinations in the Daurian Partridge from QAN, two from AHQ and three from AERS.
Tests for differences in the distribution of allele frequencies indicated highly significant (p < 0.001) differentiation between all pairs of populations. Microsatellite genetic diversity was significantly partitioned among the 23 populations (average multilocus FST = 0.10, RST = 0.11, p < 0.001). Most pairwise FST and RST values among populations were significantly different from zero (p < 0.01) (Table 4). The largest differentiation was observed: 1) between the LDE population of the Liupan Mountain and the populations of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (higher FST values between LDE and DCD, LDE and DLH, LDE and GD, LDE and DT); 2) between the LDE population and the populations of Gansu (higher FST values between LDE and SN, LDE and JY); and 3) between the populations of Inner Mongolia and population ZJC from Gansu and LDE from the Liupan Mountain (higher FST values between HJQ and ZJC, AERS and LDE) (Table 4).
| HUX | ZJC | JN | QAN | ZHX | SN | JY | GL | ML | HZ | DT | GD | DLH | DCD | LDE | GY | HJQ | AHQ | AERS | XH | WC | XHAI | KERL | |
| HUX | 0.054 | 0.029 | 0.039 | 0.056 | 0.059b | 0.097c | 0.076a | 0.034 | 0.023 | 0.061b | 0.088b | 0.063a | 0.084c | 0.165b | 0.084a | 0.112b | 0.073a | 0.118c | 0.033 | 0.026 | 0.106b | 0.111c | |
| ZJC | 4.741 | 0.037 | 0.045 | 0.055 | 0.095b | 0.109c | 0.042c | 0.053 | 0.056b | 0.086a | 0.103c | 0.122c | 0.108a | 0.099 | 0.077c | 0.196a | 0.065a | 0.092c | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.075b | 0.154c | |
| JN | 4.443 | 5.292 | 0.018 | 0.045a | 0.054a | 0.086c | 0.048 | 0.052a | 0.042 | 0.084a | 0.090c | 0.109b | 0.092a | 0.138b | 0.103b | 0.126c | 0.092c | 0.122c | 0.046 | 0.052a | 0.128c | 0.106a | |
| QAN | 4.292 | 5.271 | 4.312 | 0.071c | 0.072c | 0.071b | 0.053a | 0.033 | 0.059c | 0.096 | 0.079b | 0.125c | 0.121c | 0.157c | 0.093c | 0.099a | 0.085c | 0.086c | 0.018 | 0.035c | 0.110c | 0.106b | |
| ZHX | 4.401 | 4.215 | 3.372 | 6.610 | 0.036 | 0.144c | 0.090c | 0.093a | 0.077c | 0.115c | 0.121c | 0.132b | 0.143b | 0.137b | 0.098c | 0.102c | 0.087c | 0.114c | 0.062 | 0.065b | 0.114c | 0.153b | |
| SN | 3.500 | 4.183 | 4.401 | 4.241 | 3.972 | 0.126c | 0.105c | 0.092c | 0.055b | 0.098c | 0.094c | 0.128b | 0.104b | 0.234c | 0.131c | 0.142c | 0.116c | 0.128c | 0.071b | 0.093c | 0.158c | 0.128b | |
| JY | 3.923 | 4.041 | 5.732 | 2.532 | 2.120 | 3.052 | 0.048a | 0.043 | 0.088b | 0.121c | 0.096b | 0.121b | 0.110a | 0.229c | 0.116c | 0.109a | 0.097c | 0.100c | 0.060 | 0.082c | 0.098c | 0.132c | |
| GL | 3.577 | 3.436 | 4.473 | 2.421 | 2.471 | 2.001 | 5.371 | 0.033 | 0.074c | 0.087b | 0.079b | 0.086b | 0.097b | 0.147a | 0.120c | 0.102b | 0.088b | 0.081c | 0.055a | 0.058c | 0.106 | 0.146b | |
| ML | 3.658 | 3.304 | 2.048 | 1.475 | 1.724 | 2.323 | 4.922 | 5.562 | 0.064c | 0.058b | 0.049a | 0.079b | 0.113b | 0.151b | 0.084a | 0.086b | 0.070c | 0.071b | 0.035 | 0.044a | 0.073a | 0.090a | |
| HZ | 2.464 | 2.012 | 2.077 | 1.501 | 2.163 | 2.711 | 2.330 | 1.961 | 2.013 | 0.026 | 0.051a | 0.040a | 0.062a | 0.183c | 0.096c | 0.084c | 0.074c | 0.091c | 0.056a | 0.053a | 0.110c | 0.096c | |
| DT | 2.052 | 1.753 | 1.802 | 1.640 | 1.700 | 1.812 | 2.643 | 1.915 | 1.813 | 6.650 | 0.040 | 0.073 | 0.098a | 0.219b | 0.120b | 0.087a | 0.100c | 0.090b | 0.032 | 0.054 | 0.110b | 0.110b | |
| GD | 2.530 | 1.914 | 2.181 | 1.812 | 2.425 | 1.570 | 2.915 | 1.816 | 1.352 | 3.151 | 3.071 | 0.092b | 0.068a | 0.228c | 0.123c | 0.101c | 0.092c | 0.037 | 0.071a | 0.074a | 0.099b | 0.140b | |
| DLH | 1.730 | 1.342 | 2.642 | 1.913 | 2.302 | 1.272 | 1.626 | 1.343 | 1.822 | 1.911 | 1.791 | 2.840 | 0.132a | 0.245a | 0.131b | 0.129a | 0.133c | 0.123b | 0.080a | 0.113b | 0.155c | 0.125c | |
| DCD | 1.634 | 1.275 | 2.181 | 1.994 | 2.260 | 1.210 | 1.345 | 1.242 | 1.584 | 1.782 | 1.944 | 2.971 | 4.471 | 0.265b | 0.142c | 0.178c | 0.121c | 0.153b | 0.107c | 0.092b | 0.170b | 0.175 | |
| LDE | 1.017 | 1.433 | 1.134 | 1.291 | 1.656 | 1.031 | 1.332 | 1.311 | 1.292 | 1.113 | 1.062 | 0.942 | 1.123 | 1.040 | 0.088c | 0.148c | 0.143 | 0.211c | 0.127b | 0.086 | 0.180c | 0.127c | |
| GY | 1.563 | 1.342 | 1.782 | 1.560 | 0.812 | 1.263 | 1.443 | 1.404 | 0.840 | 0.992 | 1.760 | 1.142 | 1.390 | 1.014 | 3.602 | 0.092b | 0.075b | 0.126c | 0.050 | 0.051a | 0.092c | 0.196c | |
| HJQ | 1.703 | 2.025 | 2.083 | 1.942 | 1.331 | 1.105 | 1.302 | 2.172 | 1.314 | 1.221 | 1.361 | 1.280 | 1.321 | 1.221 | 2.461 | 1.431 | 0.021 | 0.053a | 0.027 | 0.031a | 0.041 | 0.130b | |
| AHQ | 1.721 | 1.703 | 2.181 | 2.194 | 1.515 | 1.091 | 1.290 | 1.645 | 1.055 | 1.155 | 1.679 | 1.231 | 1.612 | 1.143 | 1.483 | 1.144 | 1.890 | 0.086c | 0.038a | 0.032 | 0.066b | 0.136c | |
| AERS | 2.453 | 2.281 | 2.594 | 2.621 | 1.903 | 1.173 | 1.103 | 1.333 | 1.333 | 1.102 | 1.621 | 1.171 | 1.235 | 1.132 | 1.090 | 1.090 | 1.517 | 2.532 | 0.050a | 0.057b | 0.027 | 0.123c | |
| XH | 2.521 | 3.824 | 3.411 | 3.623 | 2.420 | 1.162 | 1.232 | 1.472 | 1.811 | 1.463 | 1.962 | 1.325 | 1.334 | 1.044 | 1.681 | 1.652 | 2.802 | 2.690 | 1.650 | 0.004 | 0.053a | 0.075a | |
| WC | 2.168 | 3.413 | 2.622 | 1.811 | 2.272 | 1.280 | 1.281 | 1.911 | 1.932 | 1.281 | 2.863 | 1.271 | 1.225 | 1.512 | 1.775 | 1.720 | 2.503 | 2.841 | 1.491 | 5.287 | 0.049a | 0.074b | |
| XHAI | 1.804 | 2.651 | 2.465 | 1.932 | 1.693 | 1.072 | 1.140 | 1.275 | 1.251 | 1.085 | 1.776 | 1.152 | 1.523 | 1.051 | 1.732 | 0.931 | 1.211 | 2.504 | 2.662 | 3.113 | 3.726 | 0.146c | |
| KERL | 1.381 | 2.105 | 1.374 | 1.384 | 1.695 | 0.993 | 1.065 | 1.522 | 1.240 | 1.170 | 1.745 | 1.030 | 1.020 | 1.141 | 1.212 | 0.637 | 1.045 | 0.867 | 1.082 | 1.322 | 1.091 | 1.091 | |
| Abbreviations as in Table 1. a 0.01 < p < 0.05, b 0.001 < p < 0.01, c p < 0.001. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
The AMOVA revealed that 81.03% of the total genetic variance resided within populations with a substantial proportion 9.19% and 9.78% of the variance being at the within-group and among-group hierarchical levels, respectively (Table 5).
| Source of variation | Variance components | Explained variance (%) | p | Fixation indices (99% CI) |
| Among groups | 0.3312 | 9.78 | 0.0107 (0.13) | FCT = 0.10979 |
| Within groups | 0.3108 | 9.19 | 0.0000 (0.07) | FSC = 0.12278 |
| Within populations | 3.3829 | 81.03 | 0.0000 (0.19) | FST = 0.20166 |
| The AMOVA was performed using both allele frequency and molecular data simultaneously with ARLEQUIN version 3.1. The p-values are the probabilities of having a more extreme variance component than the observed values by chance and are based on 1000 random permutations of the data matrix. FCT: variance fixation indices among groups; FSC: variance fixation indices among populations within groups. |
||||
Phylogenetic trees were reconstructed by UPGMA (Fig. 2). The results show that the 23 populations may form two groups (A and B), supported by a 100% bootstrap value. The 14 populations HUX, ZJC, JN, QAN, ZHX, SN, JY, GL, ML, HZ, DT, GD, DLH, DCD formed group A (Gansu Loess Plateau and Qinghai Plateau). The populations LDE, GY, WC, XH, XHAI, HJQ, AHQ, AERS, KERL, split from group A, formed group B (Liupan Mountain, Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia, the northeastern China plains and the North China plains).
We used the program STRUCTURE on the entire dataset (285 samples, eight microsatellite loci, 23 populations) where k = 1, 2, …, 23. The results were comparable with those obtained by UPMGA (Fig. 2). The most appropriate number of populations was found to be k = 2 (Table 6). Successive increases in k did not split the two major groupings into additional clusters, suggesting that the Daurian Partridge from the 23 locations can be split into two distinct genetic clusters (A and B) (Table 6). Cluster A was anchored by Daurian Partridges from HUX, JN, QAN, ZHX, JY, HZ, GD, DLH and DCD populations (q > 0.800); cluster B consisted of Daurian Partridges from LDE, AHQ, AERS, XH, XHAI and KERL populations (q > 0.800). Partridges from ZJC, SN, GL, ML, DT, GY, HJQ and WC were not assigned to any single cluster (q = 0.800), but were split into two clusters. The assignment of the individuals to the two clusters was performed without using prior population information. All the individuals from HUX, ZJC, ZHX, SN, ML, DT, GY and XH were assigned correctly to their own clusters. The percentage of assigned individuals ranged from 66.7% to 94.1% in the other populations. The global performance of STRUCTURE assigning individuals to k = 2 clusters was 252/285 = 88.4%.
| Population | A | B | Unassigned individuals | Percentage of assigned individuals (%) |
| HUX(10) | 0.881(9) | 0.119(1) | 0 | 100 |
| ZJC(15) | 0.599(9) | 0.401(6) | 0 | 100 |
| JN(13) | 0.821(9) | 0.179(2) | 2 | 84.6 |
| QAN(17) | 0.872(14) | 0.128(2) | 1 | 94.1 |
| ZHX(15) | 0.993(15) | 0.007(0) | 0 | 100 |
| SN(15) | 0.664(10) | 0.336(5) | 0 | 100 |
| JY(15) | 0.828(10) | 0.172(0) | 5 | 66.7 |
| GL(16) | 0.630(7) | 0.370(5) | 4 | 75.0 |
| ML(15) | 0.733(11) | 0.267(4) | 0 | 100 |
| HZ(11) | 0.859(8) | 0.141(1) | 2 | 81.8 |
| DT(9) | 0.772(7) | 0.228(2) | 0 | 100 |
| GD(10) | 0.811(8) | 0.189(1) | 1 | 90.0 |
| DLH(7) | 0.885(5) | 0.115(1) | 1 | 85.7 |
| DCD(10) | 0.915(7) | 0.085(0) | 3 | 70.0 |
| LDE(15) | 0.130(1) | 0.870(13) | 1 | 93.3 |
| GY(15) | 0.267(4) | 0.733(11) | 0 | 100 |
| HJQ(16) | 0.414(6) | 0.586(8) | 2 | 87.5 |
| AHQ(15) | 0.131(0) | 0.869(11) | 4 | 73.3 |
| AERS(10) | 0.188(0) | 0.812(8) | 2 | 80.0 |
| XH(7) | 0.193(2) | 0.807(5) | 0 | 100 |
| WC(8) | 0.359(2) | 0.641(4) | 2 | 75.0 |
| XHAI(16) | 0.191(3) | 0.809(11) | 2 | 87.5 |
| KERL(5) | 0.037(0) | 0.963(4) | 1 | 80.0 |
| The posterior probability of the number of populations in the sample set was maximum with k = 2. The table shows the proportion of membership (q) of each predefined sampled population in each of two inferred clusters. Each sampled populations was assigned to a single cluster if its q was equal or larger than 0.800, or to two or more clusters when the cumulative q values were equal or larger than 0.800. The number and percentage of individuals assigned to their original population with a probability threshold of 0.800 are indicated in parentheses. The unassigned individuals were assigned to more than one cluster with probability lower than 0.800. Abbreviations as in Table 1. |
||||
A MANTEL test was performed to check for isolation by distance using FST/(1−FST) as recommended by Rousset (1997). Correlations between relatedness and geographic distance were analyzed among sampled populations (Fig. 3). Positive values of r were observed among the populations. There were no significant correlations between geographic populations FST/(1−FST) pairwise and geographic distance (r = 0.179, r2 = 0.032, p > 0.05).
Bottleneck tests showed significant deviations for mutation-drift equilibrium under the IAM (14 out of 23 populations), the SMM (six out of 23 populations) and TPM (nine out of 23 populations), which suggest a recent decline in population size. The discrepancy between the three models was probably caused by different heterozygosities at the mutation equilibrium (Luikart and Cornuet, 1997). Given that few microsatellite loci are expected to evolve strictly according to a one-step SMM and IAM, the TPM is recommended (Di Rienzo et al., 1994). It is reasonable to believe that recent demographic bottlenecks have occurred in the Daurian Partridge, although the possibility cannot be ruled out that the results might be biased due to deviation from HWE (Table 7). From a comprehensive considering of the results of the three models, we conclude that the HUX, SN, GY and XH populations have recently experienced a significant decline.
| Population | IAM | SMM | TPM |
| HUX | 0.0059* | 0.0027* | 0.0098* |
| ZJC | 0.1326 | 0.0039* | 0.0039* |
| JN | 0.0039* | 0.1250 | 0.8085 |
| QAN | 0.0020* | 0.8437 | 0.0020* |
| ZHX | 0.0020* | 0.3170 | 0.0020* |
| SN | 0.0020* | 0.0039* | 0.0020* |
| JY | 0.0273 | 0.4726 | 0.2304 |
| GL | 0.1250 | 0.5781 | 0.4219 |
| ML | 0.0035* | 0.0850 | 0.0223 |
| HZ | 0.0020* | 0.2734 | 0.0097* |
| DT | 0.0273 | 0.3203 | 0.1250 |
| GD | 0.0137 | 0.3203 | 0.3203 |
| DLH | 0.1562 | 0.2305 | 0.4726 |
| DCD | 0.0977 | 0.5781 | 0.7693 |
| LDE | 0.0058* | 0.4726 | 0.0976 |
| GY | 0.0020* | 0.0039* | 0.0023* |
| HJQ | 0.0039* | 0.0137 | 0.3711 |
| AHQ | 0.0137 | 0.7265 | 0.2734 |
| AERS | 0.0020* | 0.0976 | 0.0039* |
| XH | 0.0039* | 0.0039* | 0.0039* |
| WC | 0.2891 | 0.7656 | 0.4062 |
| XHAI | 0.0020* | 0.0020* | 0.0976 |
| KERL | 0.0020* | 0.0390 | 0.1146 |
| IAM, infinite allele model; SMM, stepwise mutation model; TPM, two-phased model of mutation. Abbreviations as in Table 1. * population which has experienced bottleneck. |
|||
Based on PIC values, the microsatellite primers used in the present study have proved to be highly polymorphic in nature and hence can be effectively used for molecular characterization of the Daurian Partridge. In general, the PIC values are suggestive of a highly polymorphic nature of the microsatellite loci analyzed. This refers to the value of a marker for detecting polymorphism within a population, depending upon the number of detectable alleles and the distribution of their frequency and has proved to be a general measure of how informative a marker is (Ramamoorthi et al., 2009).
There is a dearth of published reports on the number of alleles, their sizes and frequencies for these microsatellite loci in the Daurian Partridge. The number of alleles available from scanning the literature was three for MCW323, 13 for AF12114 in Alectoris magna (Chen et al., 2006) and 14 for MCW323, 20 for AF12114, 21 for UBC0002, 11 for UBC0006 in the Tibetan Snowcock (An et al., 2009). There are some differences in the number of alleles with the Daurian Partridge. The greater the number of alleles at any given locus, the more informative will be the marker (Ramamoorthi et al., 2009).
High levels of genetic diversity were found in the Daurian Partridge populations. We can see that the gene flow was very common among all Daurian Partridge populations and the value of Nm was at a high level. The Nm values were larger than one in nearly all pairs of populations; for many pairs of populations, the values were as high as four or five (Table 4). We hypothesize two main factors that are the most likely reasons for the genetic structure of this species. First, the Daurian Partridge is a kind of bird widely distributed in northern China with wide ecological differentiations. The partridge inhabits meadows, shrubby areas, plantations, river valleys, open mountain slopes and subalpine meadows. The distribution area contains arid districts, semi-arid, semi-humid and humid regions. High levels of genetic diversity in natural populations are associated with a wide range of ecological types and niche variation (Prentice et al., 1995). Habitat fragmentation and deterioration resulting from Quaternary glaciations, following an arid trend and human activities of northern China, are most likely factors leading to high genetic diversity and high population differentiation in this species (Tables 3 and 4). Besides, following the gradual weakening of the geographic barriers for Daurian Partridge, now the common gene flow makes for excellent high level genotype exchanges.
Some populations are deficient in heterozygotes (p < 0.001; Table 3). A heterozygote deficit might, in part, be a consequence of null alleles or allelic dropout. In our dataset all locus combinations were likely contributors to heterozygous deficits, which experienced the Wahlund effect (Hartl and Clark, 1997) resulting from geographic populations that were isolated from one another to varying degrees and therefore genetically differentiated.
Between-population comparisons of mean expected heterozygosity and mean allelic richness revealed that the levels of genetic diversity were significantly different in some estimated populations. The Qaidam Basin is surrounded by several mountains and some references have demonstrated that the Qaidam Basin was a refuge during the last Ice Age (Chen et al., 1999; Hou et al., 2002; Liu et al., 2004; Huang and Liu, 2007). We hypothesize that the Qaidam Basin may also be a refuge for the Daurian Partridge, which has had a great diversity of ancestors, so that populations from the Qaidam Basin (DLH, DCD) have a high level of genetic diversity. The JN and ZJC populations from the Lanzhou Basin also have a high level of diversity, which may have resulted from the mountain barriers. The Lanzhou Basin may have been a refuge during the last Ice Age (Liu et al., 2004; Huang and Liu, 2007) for the Daurian Partridge as well. The North China populations, especially WC, have high levels of diversity, probably caused by a suitable living environment. The Liupan Mountain populations have a low level of alleles and allelic richness but the highest level of unique alleles and we speculate that, because the Liupan Mountain region has abundant precipitation, it formed a local micro-climate (Liu et al., 1988). The genetic differences between populations from the Liupan Mountain with other populations were more pronounced. The XHAI population has a low level of diversity, most likely owing to its cold environment and excessive hunting activities by humans. The KERL population has the lowest level of diversity. We have not discovered the reason, but hypothesize that the small sample size from the KERL population may have resulted in a low reflection of genetic characteristics in its data.
Both the UPGMA clustering analysis based on DA distances between populations and the Bayesian clustering analysis of multilocus genotypes of individuals provided clear indications of genetic divergence between populations into two groups (FST = 0.12, RST = 0.13, p < 0.001). There are broad deserts in northern China, such as the Taklimakan, Kumutage, Badain Jaran, Tengger and Mu Us deserts. Considering that the Daurian Partridge is a kind of grassland species, we speculate that the broad deserts formed barriers for the spread of the partridge, restricting the gene flow between groups A and B. Populations from group A were found at higher elevations than the populations from group B. The Qinghai and Gansu Loess plateaus are drier and colder than other regions, where different living environments and selective pressure may lead to divergence between the two groups.
High genetic differentiation can reflect "isolation by distance", which implies that distance-dependent gene flows generally limit genetic differences among natural populations (Wright, 1943; Slatkin, 1993). Thus, populations which are geographically close will be genetically more similar. However, in our study, genetic and geographic distances did not show significant correlation (Table 4, Fig. 1). The effect of geographic distance on the pattern of differentiation within this species seemed to be negligible. Significant population differentiation was found both between groups and between population pairs within the same group (Table 4). Even geographically adjacent populations exhibited significant genetic differences. Quantitative analysis of genetic differentiation showed that genetic differences between populations from the Liupan Mountain with other populations investigated as well as between populations from Inner Mongolia with other populations, were larger than other population pairs. FST and RST are affected by natural selection, gene flow and migration among geographic populations (Chen et al., 2006). Migration could enhance gene flow and decrease genetic differentiation among populations. Gene flow estimates (Nm) were greater than 1 for most population pairs in our study, implying that migration among Daurian Partridge populations was so common that it counteracted the effect of random genetic drift as predicted from theoretical considerations (Slatkin, 1987).
Populations that have experienced recent population declines commonly exhibit an excess of heterozygosity, evidence for deviation from mutation-drift equilibrium. Significant excess of heterozygosity was detected in some populations, especially in HUX, SN, GY and XH. Huanxian County is located at the edge of the Mu Us desert where the environment is not suitable for the Daurian Partridge. Su'nan consists mainly of mountains and we conjecture that, because of the mountain barriers, its population might be small. Guyuan was subject to a strong earthquake in the middle of the 16th century, which might have caused a considerable decline in its partridge population. One reason for the XH population decline may be earlier over-hunting; the other reason might be the smaller sample size in our study. Conservation biologists widely agree that population bottlenecks should be avoided in species because they increase rates of inbreeding, causing loss of genetic variation and fixation of mildly deleterious alleles and thereby reduce the adaptive potential and increase the probability of extinction (Frankel and Soule, 1981).
The present study was a preliminary attempt to demonstrate the condition of genetic diversity and genetic structure in Daurian Partridges. We obtained much meaningful genetic information that should be useful in the formulation of effective conservation management strategies and identification of loci of quantitative traits for marker-assisted selection. Considering that the Liupan Mountain populations have a high level of unique alleles and genetic differences, we recommend that greater attention should be paid to these populations. Furthermore, special attention should be given to preserving the Qaidam populations, North China populations, JN population and ZJC population in order to retain an adequate population size for maintaining genetic diversity.
We are especially grateful to Dr. Peng Hou (Department of Medicine, the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine) for helpful comments on a previous version of this manuscript and for helping to improve the English. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30530130).
|
Avise JC. 1994. Molecular Markers, Natural History and Evolution. Chapman & Hall, New York
|
|
Belkhir K, Borsa P, Chikhi L, Raufaste N, Catch F. 2004. GENETIX (version 4.02), Software under WindowsTM for the genetics of the populations Laboratory Genome, Populations, Interactions, CNRS UMR 5000, University of Montpellier Ⅱ, Montpellier, France
|
|
Chen Q, Chang C, Liu NF. 1999. Mitochondrial DNA introgression between two parapatric species of Alectoris. Acta Zool Sin, 45(4): 456–463 (in Chinese)
|
|
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S. 2005. ARLEQUIN, version3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinfor Online, 1: 47–50
|
|
Frankel OH, Soule ME. 1981. Conservation and Evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England
|
|
Goudet J. 2001. FSTAT. A program to estimate and test gene diversities and fixation indices, (Version 2.9.3). Updated from Goudet (1995)
|
|
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW. 1989. Allozyme diversity in plant species. In: Brown AHD, Clegg MT, Kahler AL, Weir BS (eds) Plant Population Genetics, Breeding, and Genetic Resources. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA, pp 43–63
|
|
Hartl DL, Clark AG. 1997. Principles of Population Genetics. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA
|
|
Heuertz M, Hausman JF, Hardy OJ, Vendramin GG, Frascaria-Lacoste N, Vekemans X. 2004. Nuclear microsatellites reveal contrasting patterns of genetic structure between western and southeastern European populations of the common ash (Fraxinus excelsior L. ). Evolution, 58: 976–988
|
|
Hou P, Wei M, Zhang LX, Liu NF. 2002. Genetic structure of edge population in Przewalski's rock partridge (Alectoris magna). Acta Zool Sin, 48(3): 333–338 (in Chinese)
|
|
Johnsgard PA. 1988. The Quails, Partridges, and Francolins of the World. Oxford University Press, Oxford
|
|
Liu NF, Huang ZH, Wen LY. 2004. Subspecies divergence of Przewalski's rock partridge (Alectoris magna) description of a new subspecies. Acta Zootaxon Sin, 29(3): 600–605 (in Chinese)
|
|
Liu NF, Wang XT, Luo WY, Chang C. 1988. Avifauna study of the Liupan Mountain in Ningxia. J Lanzhou Univ Nat Sci Ed, 24: 63–75 (in Chinese)
|
|
Luikart G, Cornuet JM. 1997. Empirical evaluation of a test for identifying recently bottlenecked populations from allele frequency data. Conserv Biol, 12: 228–237
|
|
Madge S, McGowan P. 2002. Pheasants, Partridges and Grouse: A Guide to the Pheasants, Partridges, Quails, Grouse, Guineafowl, Buttonquails and Sandgrouse of the World. Christopher Helm, London
|
|
Mantel N. 1967. The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res, 27: 209–220
|
|
Nei M. 1987. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
|
|
Sun HY, Cao ZW, Jiang HL, Yu LG. 1998. Brooding and growth of the younger Perdix dauuricae. Forest Sci Technol, 23(4): 28–30 (in Chinese)
|
|
Sun HY, Ge DN, Hong YT, Cao ZW. 1996. Research about domesticating and breeding technology of Daurian Partridge (Perdix dauuricae). Forest Sci Technol, 21(4): 32–35 (in Chinese)
|
|
Turner PC, McLennan AG, Bates AD, White MRH. 2003. Instant Notes in Molecular Biology, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing
|
|
Weir BS, Cockerham CC. 1984. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution, 38: 1358–1370
|
|
Woodruff DS. 1989. The problems of conserving genes and species. In: Weston D, Pearl M (eds) Conservation for the Twenty First Century. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 76–88
|
|
Zhang ZW, Liang W, Sheng G. 1994. Studies on the nest site selection of Daurian partridge. Zool Res, 15(4): 37–43 (in Chinese)
|
|
Zhang ZW, Wu YC. 1992. The Daurian Partridge (Perdix dauuricae) in north-central China. Gibier Faune Sauvage, 9: 591–595
|
|
Zhang ZW, Liang W. 1997. Breeding ecology of Daurian Partridge (Perdix dauuricae) in Shanxi. Chinese J Zool, 2(2): 23–25 (in Chinese)
|
|
Zhao ZJ, Zhang S, Feng KF. 1992. The biology of the Daurian Partridge (Perdix dauuricae suschkini) in northeastern China. Gibier Faune Sauvage, 9: 597–604
|
|
Zheng ZX. 1978. Fauna Sinica. Aves. Galliformes. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
|
| Population number |
Location | Abbreviation | Group name | Latitude | Longitude | Sample size |
| Gansu Loess Plateau | ||||||
| 1 | Huanxian County | HUX | A | 36°55.37′ | 101°41.08′ | 10 |
| 2 | Zhangjiachuan | ZJC | A | 34°59.41′ | 106°12.43′ | 15 |
| 3 | Jingning | JN | A | 35°31.19′ | 105°43.57′ | 13 |
| 4 | Qin'an | QAN | A | 34°51.31′ | 105°40.10′ | 17 |
| 5 | Zhangxian County | ZHX | A | 34°50.78′ | 104°27.89′ | 15 |
| 6 | Su'nan | SN | A | 38°50.13′ | 99°36.56′ | 15 |
| 7 | Jingyuan | JY | A | 37°57.46′ | 101°35.07′ | 15 |
| 8 | Gulang | GL | A | 37°28.13′ | 102°53.51′ | 16 |
| 9 | Minle | ML | A | 38°25.50′ | 100°48.46′ | 15 |
| Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau | ||||||
| 10 | Huzhu | HZ | A | 37°7.07′ | 100°17.51′ | 11 |
| 11 | Datong | DT | A | 36°51.07′ | 102°9.07′ | 9 |
| 12 | Guide | GD | A | 35°56.03′ | 101°28.37′ | 10 |
| 13 | Delingha | DLH | A | 32°22.13′ | 97°21.24′ | 7 |
| 14 | Dachaidan | DCD | A | 37°50.01′ | 95°17.53′ | 10 |
| Liupan Mountain | ||||||
| 15 | Longde | LDE | B | 35°33.21′ | 106°2.46′ | 15 |
| 16 | Guyuan | GY | B | 36°1.00′ | 106°14.34′ | 15 |
| Inner Mongolia | ||||||
| 17 | Hangjinqi | HJQ | B | 39°50.55′ | 108°43.49′ | 16 |
| 18 | Aohanqi | AHQ | B | 42°17.05′ | 119°54.00′ | 15 |
| 19 | Aershan | AERS | B | 47°10.39′ | 119°56.37′ | 10 |
| North China Plain | ||||||
| 20 | Xuanhua | XH | B | 40°29.33′ | 115°6.19′ | 7 |
| 21 | Weichang | WC | B | 42°5.38′ | 117°31.39′ | 8 |
| Northeast China Plain | ||||||
| 22 | Xianghai | XHAI | B | 45°1.84′ | 122°24.34′ | 16 |
| Xinjiang | ||||||
| 23 | Kuerler | KERL | B | 41°45.35′ | 86°8.05′ | 5 |
| The group names A and B correspond to the cluster names in Fig. 2. | ||||||
| Locus | TA | PIC | HT | HS | HO | FIS |
| MCW104 | 14 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.333*** |
| MCW280 | 5 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 0.309** |
| AF12114 | 11 | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.42 | 0.401 |
| UBC0006 | 20 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.78 | 0.185** |
| UBC0002 | 7 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.51 | 0.348** |
| GUJ0059 | 13 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.60 | 0.346*** |
| GUJ0049 | 9 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.325* |
| MCW323 | 15 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.338*** |
| Average | 11.75 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.58 | 0.323*** |
|
TA, total number of alleles; PIC, polymorphic information content; HT, gene diversity in the total population; HS, average gene diversity within populations; HO, observed heterozygosity; FIS, fixation index. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. |
||||||
| Population | A | AR | Na | p | HO (SD) | HE (SD) | FIS (95% CI) |
| HUX | 7.3 | 6.50 | 3 | 8.00 | 0.55 (0.32) | 0.71 (0.21) | 0.074 (0.122–0.206) * |
| ZJC | 8.0 | 7.00 | 1 | 8.00 | 0.63 (0.29) | 0.68 (0.15) | 0.084 (0.119–0.215) * |
| JN | 8.0 | 7.00 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.66 (0.27) | 0.70 (0.09) | 0.086 (0.105–0.218) |
| QAN | 7.6 | 7.00 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.62 (0.27) | 0.71 (0.16) | 0.102 (0.107–0.325) * |
| ZHX | 7.5 | 7.00 | 0 | 7.00 | 0.58 (0.29) | 0.70 (0.14) | 0.087 (0.109–0.277) |
| SN | 7.8 | 7.00 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.60 (0.22) | 0.70 (0.22) | 0.071 (0.087–0.160) |
| JY | 7.9 | 7.15 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.56 (0.39) | 0.69 (0.19) | 0.075 (0.075–0.198) |
| GL | 7.0 | 5.95 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.58 (0.33) | 0.67 (0.22) | 0.069 (0.104–0.198) * |
| ML | 7.4 | 7.00 | 4 | 7.00 | 0.59 (0.11) | 0.62 (0.07) | 0.086 (0.195–0.396) |
| HZ | 7.0 | 6.25 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.53 (0.29) | 0.71 (0.13) | 0.092 (0.136–0.249) |
| DT | 7.0 | 6.75 | 0 | 8.00 | 0.60 (0.35) | 0.72 (0.10) | 0.073 (0.046–0.165) |
| GD | 7.1 | 6.50 | 3 | 8.00 | 0.58 (0.24) | 0.76 (0.12) | 0.084 (0.137–0.275) * |
| DLH | 8.0 | 7.55 | 5 | 8.00 | 0.67 (0.31) | 0.81 (0.11) | 0.086 (0.052–0.122) |
| DCD | 8.9 | 8.05 | 3 | 8.00 | 0.70 (0.35) | 0.78 (0.07) | 0.075 (0.021–0.200) |
| LDE | 6.1 | 5.00 | 6 | 8.00 | 0.52 (0.29) | 0.72 (0.11) | 0.087 (–0.043–0.500)* |
| GY | 6.4 | 5.75 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.56 (0.24) | 0.70 (0.13) | 0.069 (0.109–0.202) |
| HJQ | 7.0 | 6.25 | 3 | 7.00 | 0.57 (0.31) | 0.71 (0.21) | 0.097 (0.025–0.107) |
| AHQ | 7.8 | 6.75 | 1 | 8.00 | 0.53 (0.32) | 0.61 (0.25) | 0.088 (0.163–0.229) * |
| AERS | 7.3 | 6.05 | 4 | 8.00 | 0.61 (0.24) | 0.72 (0.15) | 0.067 (0.087–0.139) |
| XH | 7.0 | 6.35 | 3 | 8.00 | 0.64 (0.28) | 0.76 (0.10) | 0.071 (0.128–0.226) |
| WC | 8.7 | 8.00 | 2 | 7.00 | 0.68 (0.30) | 0.76 (0.07) | 0.112 (0.151–0.218) |
| XHAI | 7.2 | 6.25 | 2 | 8.00 | 0.46 (0.42) | 0.70 (0.17) | 0.092 (0.112–0.257) |
| KERL | 4.3 | 3.50 | 4 | 7.00 | 0.42 (0.29) | 0.70 (0.09) | 0.084 (0.025–0.231) |
| Total | – | – | – | 8 | 0.58 (0.34) | 0.72 (0.17) | 0.333 (0.201–0.379) |
| Abbreviations as in Table 1. * significant (p < 0.001) departures from HWE tested by multilocus probability test using GENEPOP. |
|||||||
| HUX | ZJC | JN | QAN | ZHX | SN | JY | GL | ML | HZ | DT | GD | DLH | DCD | LDE | GY | HJQ | AHQ | AERS | XH | WC | XHAI | KERL | |
| HUX | 0.054 | 0.029 | 0.039 | 0.056 | 0.059b | 0.097c | 0.076a | 0.034 | 0.023 | 0.061b | 0.088b | 0.063a | 0.084c | 0.165b | 0.084a | 0.112b | 0.073a | 0.118c | 0.033 | 0.026 | 0.106b | 0.111c | |
| ZJC | 4.741 | 0.037 | 0.045 | 0.055 | 0.095b | 0.109c | 0.042c | 0.053 | 0.056b | 0.086a | 0.103c | 0.122c | 0.108a | 0.099 | 0.077c | 0.196a | 0.065a | 0.092c | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.075b | 0.154c | |
| JN | 4.443 | 5.292 | 0.018 | 0.045a | 0.054a | 0.086c | 0.048 | 0.052a | 0.042 | 0.084a | 0.090c | 0.109b | 0.092a | 0.138b | 0.103b | 0.126c | 0.092c | 0.122c | 0.046 | 0.052a | 0.128c | 0.106a | |
| QAN | 4.292 | 5.271 | 4.312 | 0.071c | 0.072c | 0.071b | 0.053a | 0.033 | 0.059c | 0.096 | 0.079b | 0.125c | 0.121c | 0.157c | 0.093c | 0.099a | 0.085c | 0.086c | 0.018 | 0.035c | 0.110c | 0.106b | |
| ZHX | 4.401 | 4.215 | 3.372 | 6.610 | 0.036 | 0.144c | 0.090c | 0.093a | 0.077c | 0.115c | 0.121c | 0.132b | 0.143b | 0.137b | 0.098c | 0.102c | 0.087c | 0.114c | 0.062 | 0.065b | 0.114c | 0.153b | |
| SN | 3.500 | 4.183 | 4.401 | 4.241 | 3.972 | 0.126c | 0.105c | 0.092c | 0.055b | 0.098c | 0.094c | 0.128b | 0.104b | 0.234c | 0.131c | 0.142c | 0.116c | 0.128c | 0.071b | 0.093c | 0.158c | 0.128b | |
| JY | 3.923 | 4.041 | 5.732 | 2.532 | 2.120 | 3.052 | 0.048a | 0.043 | 0.088b | 0.121c | 0.096b | 0.121b | 0.110a | 0.229c | 0.116c | 0.109a | 0.097c | 0.100c | 0.060 | 0.082c | 0.098c | 0.132c | |
| GL | 3.577 | 3.436 | 4.473 | 2.421 | 2.471 | 2.001 | 5.371 | 0.033 | 0.074c | 0.087b | 0.079b | 0.086b | 0.097b | 0.147a | 0.120c | 0.102b | 0.088b | 0.081c | 0.055a | 0.058c | 0.106 | 0.146b | |
| ML | 3.658 | 3.304 | 2.048 | 1.475 | 1.724 | 2.323 | 4.922 | 5.562 | 0.064c | 0.058b | 0.049a | 0.079b | 0.113b | 0.151b | 0.084a | 0.086b | 0.070c | 0.071b | 0.035 | 0.044a | 0.073a | 0.090a | |
| HZ | 2.464 | 2.012 | 2.077 | 1.501 | 2.163 | 2.711 | 2.330 | 1.961 | 2.013 | 0.026 | 0.051a | 0.040a | 0.062a | 0.183c | 0.096c | 0.084c | 0.074c | 0.091c | 0.056a | 0.053a | 0.110c | 0.096c | |
| DT | 2.052 | 1.753 | 1.802 | 1.640 | 1.700 | 1.812 | 2.643 | 1.915 | 1.813 | 6.650 | 0.040 | 0.073 | 0.098a | 0.219b | 0.120b | 0.087a | 0.100c | 0.090b | 0.032 | 0.054 | 0.110b | 0.110b | |
| GD | 2.530 | 1.914 | 2.181 | 1.812 | 2.425 | 1.570 | 2.915 | 1.816 | 1.352 | 3.151 | 3.071 | 0.092b | 0.068a | 0.228c | 0.123c | 0.101c | 0.092c | 0.037 | 0.071a | 0.074a | 0.099b | 0.140b | |
| DLH | 1.730 | 1.342 | 2.642 | 1.913 | 2.302 | 1.272 | 1.626 | 1.343 | 1.822 | 1.911 | 1.791 | 2.840 | 0.132a | 0.245a | 0.131b | 0.129a | 0.133c | 0.123b | 0.080a | 0.113b | 0.155c | 0.125c | |
| DCD | 1.634 | 1.275 | 2.181 | 1.994 | 2.260 | 1.210 | 1.345 | 1.242 | 1.584 | 1.782 | 1.944 | 2.971 | 4.471 | 0.265b | 0.142c | 0.178c | 0.121c | 0.153b | 0.107c | 0.092b | 0.170b | 0.175 | |
| LDE | 1.017 | 1.433 | 1.134 | 1.291 | 1.656 | 1.031 | 1.332 | 1.311 | 1.292 | 1.113 | 1.062 | 0.942 | 1.123 | 1.040 | 0.088c | 0.148c | 0.143 | 0.211c | 0.127b | 0.086 | 0.180c | 0.127c | |
| GY | 1.563 | 1.342 | 1.782 | 1.560 | 0.812 | 1.263 | 1.443 | 1.404 | 0.840 | 0.992 | 1.760 | 1.142 | 1.390 | 1.014 | 3.602 | 0.092b | 0.075b | 0.126c | 0.050 | 0.051a | 0.092c | 0.196c | |
| HJQ | 1.703 | 2.025 | 2.083 | 1.942 | 1.331 | 1.105 | 1.302 | 2.172 | 1.314 | 1.221 | 1.361 | 1.280 | 1.321 | 1.221 | 2.461 | 1.431 | 0.021 | 0.053a | 0.027 | 0.031a | 0.041 | 0.130b | |
| AHQ | 1.721 | 1.703 | 2.181 | 2.194 | 1.515 | 1.091 | 1.290 | 1.645 | 1.055 | 1.155 | 1.679 | 1.231 | 1.612 | 1.143 | 1.483 | 1.144 | 1.890 | 0.086c | 0.038a | 0.032 | 0.066b | 0.136c | |
| AERS | 2.453 | 2.281 | 2.594 | 2.621 | 1.903 | 1.173 | 1.103 | 1.333 | 1.333 | 1.102 | 1.621 | 1.171 | 1.235 | 1.132 | 1.090 | 1.090 | 1.517 | 2.532 | 0.050a | 0.057b | 0.027 | 0.123c | |
| XH | 2.521 | 3.824 | 3.411 | 3.623 | 2.420 | 1.162 | 1.232 | 1.472 | 1.811 | 1.463 | 1.962 | 1.325 | 1.334 | 1.044 | 1.681 | 1.652 | 2.802 | 2.690 | 1.650 | 0.004 | 0.053a | 0.075a | |
| WC | 2.168 | 3.413 | 2.622 | 1.811 | 2.272 | 1.280 | 1.281 | 1.911 | 1.932 | 1.281 | 2.863 | 1.271 | 1.225 | 1.512 | 1.775 | 1.720 | 2.503 | 2.841 | 1.491 | 5.287 | 0.049a | 0.074b | |
| XHAI | 1.804 | 2.651 | 2.465 | 1.932 | 1.693 | 1.072 | 1.140 | 1.275 | 1.251 | 1.085 | 1.776 | 1.152 | 1.523 | 1.051 | 1.732 | 0.931 | 1.211 | 2.504 | 2.662 | 3.113 | 3.726 | 0.146c | |
| KERL | 1.381 | 2.105 | 1.374 | 1.384 | 1.695 | 0.993 | 1.065 | 1.522 | 1.240 | 1.170 | 1.745 | 1.030 | 1.020 | 1.141 | 1.212 | 0.637 | 1.045 | 0.867 | 1.082 | 1.322 | 1.091 | 1.091 | |
| Abbreviations as in Table 1. a 0.01 < p < 0.05, b 0.001 < p < 0.01, c p < 0.001. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source of variation | Variance components | Explained variance (%) | p | Fixation indices (99% CI) |
| Among groups | 0.3312 | 9.78 | 0.0107 (0.13) | FCT = 0.10979 |
| Within groups | 0.3108 | 9.19 | 0.0000 (0.07) | FSC = 0.12278 |
| Within populations | 3.3829 | 81.03 | 0.0000 (0.19) | FST = 0.20166 |
| The AMOVA was performed using both allele frequency and molecular data simultaneously with ARLEQUIN version 3.1. The p-values are the probabilities of having a more extreme variance component than the observed values by chance and are based on 1000 random permutations of the data matrix. FCT: variance fixation indices among groups; FSC: variance fixation indices among populations within groups. |
||||
| Population | A | B | Unassigned individuals | Percentage of assigned individuals (%) |
| HUX(10) | 0.881(9) | 0.119(1) | 0 | 100 |
| ZJC(15) | 0.599(9) | 0.401(6) | 0 | 100 |
| JN(13) | 0.821(9) | 0.179(2) | 2 | 84.6 |
| QAN(17) | 0.872(14) | 0.128(2) | 1 | 94.1 |
| ZHX(15) | 0.993(15) | 0.007(0) | 0 | 100 |
| SN(15) | 0.664(10) | 0.336(5) | 0 | 100 |
| JY(15) | 0.828(10) | 0.172(0) | 5 | 66.7 |
| GL(16) | 0.630(7) | 0.370(5) | 4 | 75.0 |
| ML(15) | 0.733(11) | 0.267(4) | 0 | 100 |
| HZ(11) | 0.859(8) | 0.141(1) | 2 | 81.8 |
| DT(9) | 0.772(7) | 0.228(2) | 0 | 100 |
| GD(10) | 0.811(8) | 0.189(1) | 1 | 90.0 |
| DLH(7) | 0.885(5) | 0.115(1) | 1 | 85.7 |
| DCD(10) | 0.915(7) | 0.085(0) | 3 | 70.0 |
| LDE(15) | 0.130(1) | 0.870(13) | 1 | 93.3 |
| GY(15) | 0.267(4) | 0.733(11) | 0 | 100 |
| HJQ(16) | 0.414(6) | 0.586(8) | 2 | 87.5 |
| AHQ(15) | 0.131(0) | 0.869(11) | 4 | 73.3 |
| AERS(10) | 0.188(0) | 0.812(8) | 2 | 80.0 |
| XH(7) | 0.193(2) | 0.807(5) | 0 | 100 |
| WC(8) | 0.359(2) | 0.641(4) | 2 | 75.0 |
| XHAI(16) | 0.191(3) | 0.809(11) | 2 | 87.5 |
| KERL(5) | 0.037(0) | 0.963(4) | 1 | 80.0 |
| The posterior probability of the number of populations in the sample set was maximum with k = 2. The table shows the proportion of membership (q) of each predefined sampled population in each of two inferred clusters. Each sampled populations was assigned to a single cluster if its q was equal or larger than 0.800, or to two or more clusters when the cumulative q values were equal or larger than 0.800. The number and percentage of individuals assigned to their original population with a probability threshold of 0.800 are indicated in parentheses. The unassigned individuals were assigned to more than one cluster with probability lower than 0.800. Abbreviations as in Table 1. |
||||
| Population | IAM | SMM | TPM |
| HUX | 0.0059* | 0.0027* | 0.0098* |
| ZJC | 0.1326 | 0.0039* | 0.0039* |
| JN | 0.0039* | 0.1250 | 0.8085 |
| QAN | 0.0020* | 0.8437 | 0.0020* |
| ZHX | 0.0020* | 0.3170 | 0.0020* |
| SN | 0.0020* | 0.0039* | 0.0020* |
| JY | 0.0273 | 0.4726 | 0.2304 |
| GL | 0.1250 | 0.5781 | 0.4219 |
| ML | 0.0035* | 0.0850 | 0.0223 |
| HZ | 0.0020* | 0.2734 | 0.0097* |
| DT | 0.0273 | 0.3203 | 0.1250 |
| GD | 0.0137 | 0.3203 | 0.3203 |
| DLH | 0.1562 | 0.2305 | 0.4726 |
| DCD | 0.0977 | 0.5781 | 0.7693 |
| LDE | 0.0058* | 0.4726 | 0.0976 |
| GY | 0.0020* | 0.0039* | 0.0023* |
| HJQ | 0.0039* | 0.0137 | 0.3711 |
| AHQ | 0.0137 | 0.7265 | 0.2734 |
| AERS | 0.0020* | 0.0976 | 0.0039* |
| XH | 0.0039* | 0.0039* | 0.0039* |
| WC | 0.2891 | 0.7656 | 0.4062 |
| XHAI | 0.0020* | 0.0020* | 0.0976 |
| KERL | 0.0020* | 0.0390 | 0.1146 |
| IAM, infinite allele model; SMM, stepwise mutation model; TPM, two-phased model of mutation. Abbreviations as in Table 1. * population which has experienced bottleneck. |
|||